Chichester, west Sussex, England, UK 作者: 来源: 发布时间:2021-07-27
I. Population and Area
Continent: Europe
Country: The U.K
State/Province: England
City/Town: Chichester, west Sussex
Total Area: 4.12 (sq mi)
Population in 2018: 2.69 (thousand)

II. Natural Geography (environment and resources)
Climate
Chichester has a maritime climate. With its position in southern England, Chichester has mild winters and cool summers. West Sussex has high sunshine levels compared with other parts of the UK with around 1,900 hours annually
Roads
Chichester is the hub of several main roads. The most important of these is the A27 coastal trunk road (connecting Eastbourne with Southampton) which passes to the south of the city. The A27 connects Chichester to the M27, M3 and M275 motorways. The secondary coastal road, the A259, which began its journey at Folkestone in Kent, joins the A27 here and ends in Havant to the west. Both those roads make east–west connections. Three roads give Chichester access to the north: the A29 to London joins the A27 several miles to the east of the city; the A285 runs northeast to Petworth and beyond; and the A286 runs northwards towards Haslemere, Surrey.
Rail
Chichester railway station, on the West Coastway Line, has regular services to Brighton, London Victoria via Gatwick Airport, Portsmouth and Southampton. In the past there was a branch line to Midhurst in the north; and a light railway built by Colonel HF Stephens known as the West Sussex Railway which ran south to Selsey, and which closed in 1935.
Buses
There are many bus services, with Chichester bus station, adjacent to the railway station, acting as a local hub. Operators include Stagecoach in the South Downs and Compass Travel.National Express's Poole-Gatwick Airport route passes through Chichester.
Cycles
There are several long-distance routes for walkers, cyclists and riders in the area, some of which, like the Centurion Way to West Dean, start here. Centurion Way was opened in the mid-1990s and runs along the former railway line. The name was chosen by Ben Adams, a local schoolboy who won a competition to name the path.

III.Economy
Quarter 2 - September 2017
The latest data for Gross Value Added (GVA) was released in December 2016 and covers the period up to 2015. The next release of this data from ONS is expected in is a recognised measure of economic activity broadly defined as the difference between the value of the goods and services produced and the cost of raw materials and other inputs used in production. The data is released annually from ONS, and includes the sub-regional estimates for GVA for the two West Sussex Sub Areas:
The latest data,already reported, was released in December 2016, and covers the period up to2015, the figures and trends for the two West Sussex areas were reported at theend of the previous quarter and there is no update in terms of the localpicture. The next release of data is expected in December 2017. However, in March 2017 tables showing GVA allocated tolocal authorities in the UK were released, the data was produced in response touser need but while not National Statistics, nevertheless give some indicationas to the scale of GVA at local authority level, and the contribution that eachof the broad level sectors make to the local economy.
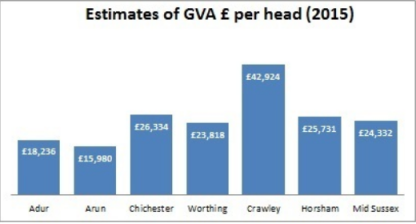
Chichester: 26334£ in 2015
Reference Website:
https://www.ons.gov.uk/economy/grossvalueaddedgva/datasets/regionalgvaibylocalauthorityintheuk
IV. Industrial Characterisitics
Major industries:
t is useful to understand local economic strengths by comparing the distribution of employment by sector in local
authority areas with the national distribution. This is performed by using Location Quotients (LQ). Any LQ above 1.0
shows a local concentration and any below 1.0 shows an under representation.
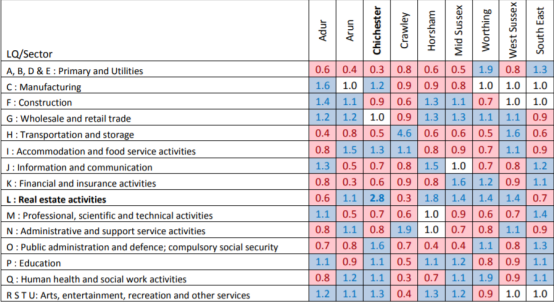
As can be seen from the above table, Chichester has local concentration in many sectors, including real estate activities, accommodation and food service activities and public administration and defence. Whilst real estate shows the highest LQ value (2.8) it is worth noting that this is still a relatively small sector with a total of 4.7% of all employee jobs. Chichester has under representation in the other industries, particularly transportation and storage, primary and utilities and finance and insurance. Wholesale and retail remain on a par with the national average.
Major projects and related introductions:
University of Chichester leading £11million project to benefit south of England
According to the university, the initiative, known as the Business Hot House programme, is offering to support more than 1,000 firms – large and small – and 500 start-up entrepreneurs to improve productivity and innovation.
The project will be delivered by the University of Chichester alongside Sussex Innovation Centre, Eastbourne and District Enterprise Agency, Brighton and Hove City Council, WSX Enterprise, Princes Trust, and YTKO Ltd.
A spokesman continued: "The multi-million pound grant was awarded by the European Regional Development Fund to develop businesses in the Coast to Capital Local Economic Partnership area, which covers West Sussex and parts of East Sussex and East Surrey."
Reference Website:
https://www.westsussex.gov.uk/media/10957/employment_trends_chichester.pdf
https://www.chichester.co.uk/business/university-chichester-leading-ps11million-project-benefit-south-england-1304163
V. Attractions
1. Chichester Cathedral:

A rousing mix of Norman Romanesque and Gothic architecture, Chichester Cathedral was started in 1075 and consecrated in 1108. It is quite unlike other English cathedrals for its twin aisles and because it has a campanile. You’ll have no trouble telling which parts of the building are original as they have Romanesque semi-circular window openings and arches.
2. Pallant House Gallery:

When he passed away in 1985, the priest and avid art collector Water Hussey left his considerable collection to the city. This was all on the condition that these works be displayed at Pallant House, a gorgeous 18th-century Queen Anne-style townhouse. A new multimillion-pound wing was added in the 2000s, funded by the Heritage Lottery Fund.
3. Fishbourne Roman Palace:

On the southwestern edge of Chichester sits the largest Roman residence unearthed in Britain.
The Fishbourne Roman Palace is also remarkable for its age, dating to AD 75, just three decades after the Roman Conquest of Britain. The palace was excavated in the 1960s, and was revealed to be about the same size as Nero’s Golden House in Rome.
Reference Website:
https://www.thecrazytourist.com/15-best-things-to-do-in-chichester-west-sussex-england/
VI. History
The area around Chichester is believed to have played significant part during the Roman invasion of AD 43, as confirmed by evidence of military storage structures in the area of the nearby Fishbourne Roman Palace. The city centre stands on the foundations of the Romano-British city of Noviomagus Reginorum, capital of the Civitas Reginorum. The Roman road of Stane Street, connecting the city with London, started at the east gate, while the Chichester to Silchester road started from the north gate. The plan of the city is inherited from the Romans: the North, South, East and West shopping streets radiate from the central market cross dating from medieval times.
he city was also home to some Roman baths, found down Tower Street when preparation for a new car park was underway. A museum, The Novium, preserving the baths was opened on 8 July 2012.
According to the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle it was captured towards the close of the fifth century, by Ælle, and renamed after his son, Cissa. It was the chief city of the Kingdom of Sussex. The cathedral for the South Saxons was founded in 681 at Selsey; the seat of the bishopric was moved to Chichester in 1075.
When the Domesday Book was compiled, Cicestre (Chichester) consisted of 300 dwellings which held a population of 1,500 people. There was a mill named Kings Mill that would have been rented to local slaves and villeins. After the Battle of Hastings the township of Chichester was handed to Roger de Mongomerie, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, for courageous efforts in the battle, but it was forfeited in 1104 by the 3rd Earl. Shortly after 1066 Chichester Castle was built by Roger de Mongomerie to consolidate Norman power. In around 1143 the title Earl of Arundel (also known as the Earl of Sussex until that title fell out of use) was created and became the dominant local landowner. In 1216, Chichester Castle, along with Reigate Castle, was captured by the French, but regained the following year, when the castle was ordered to be destroyed by the king. Between 1250 and 1262, the Rape of Chichester was created from the western half of Arundel rape, with the castle as its administrative centre.
VII. Culture
The city holds an annual four-week arts and music festival ("Festival of Chichester") held in June and July.
Chichester Festival Theatre, is one of the United Kingdom's flagship producing and touring theatres, whose annual summer season attracts actors, writers and directors from the West End theatre and the USA.
Pallant House Gallery winner of the 2007 gallery of the year Gulbenkian Prize, has a major collection of chiefly modern British art and in 2006 opened a new extension that houses the collection of Professor Sir Colin St John Wilson. It has a changing programme of exhibitions.
Chichester is home to the South Downs Planetarium & Science Centre, which opened in 2001 and features a program of public star shows in its 100-seat theatre.
The Sloe Fair, a funfair that dates back to the 12th Century, is held annually on 20 October in the city's Northgate car park.
Chichester Cinema at New Park is the city's first and only arthouse cinema. It shows a selection of mainstream, small-budget and older films 7 days a week. It hosts an annual 18-day International Film Festival in August/September. Vice-presidents are Dame Maggie Smith and Kenneth Branagh. There is a larger, multiplex cinema located at Chichester Gate.
The Chichester Open Mic has supported regular programmes of readings by contemporary poets in the city since 2010. It also hosts a high-profile annual event under the banner Poetry and All That Jazz which included performances by Don Paterson in 2010, Sam Willetts in 2011 and David Harsent in 2012.
VIII. Other information
Chichester City F.C. is the main football club and are based at Oaklands Park. They play in the Sussex County League. The rugby club, Chichester R.F.C., are also based at Oaklands Park.
Chichester Priory Park Cricket Club and Chichester Priory Park Hockey Club share a clubhouse at Priory Park.
The city is home to the Chichester Sharks Flag American Football Club who are members of the BAFA National League.In October 2007, the Sharks won the National Championship, beating Andover Voodoo 31–29 in the final. The Chichester Sharks also won the title in 2003.
Chichester Falcons Softball Club, based at Oaklands Park, play in the Solent Softball League.
Chichester Bowls Club in Priory Park is the oldest established bowls club in Sussex, being founded in 1881.
The city has a leisure centre with swimming pool, flume, sports hall and fitness room; Chichester Cormorants swimming club is based there. Chichester Runners and A.C is a club with runners and athletes from all ages. Other sports include cycling.
IX. Contact information
Mayor/Officer: Richard Plowman
Tel: 01243 788502
Mail: clerk@chichestercity.gov.uk
Reference Website:
https://chichestercity.gov.uk/open-letter-from-the-mayor-of-chichester-14-may-2020/
