Brańsk- Podlaskie 作者: 来源: 发布时间:2021-10-22
Ⅰ. Population and Area
Population (2007)
• Total 3,822
• Density 120/km2 (310/sq mi)
Area
• Total 32.43 km2 (12.52 sq mi)
Website http://www.bransk.podlaskie.pl

Ⅱ.Natural Geography (environment and resources)
-Location
-Brańsk is located in the geographical region of Europe known as the Wysoczyzny Podlasko – Bialoruskie and the mesoregion known as the Bielsk Plain (Polish: Równinę Bielską). The Nurzec River, a tributary of the Bug River, passes through Brańsk. The town covers an area of 32.43 square kilometres (12.5 sq mi).
-It is located approximately:
-140 kilometres (87.0 mi) northeast of Warsaw, the capital of Poland
-69 kilometres (42.9 mi) southwest of Białystok, the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship
-25 kilometres (15.5 mi) west of Bielsk Podlaski, the seat of Bielsk County
-Transport
-Roads and highways
-Brańsk is at the intersection of a National Road and a Voivodeship Road:
-National Road DK 66 - Zambrów - Brańsk - Bielsk Podlaski - Kleszczele - Czeremcha - Połowce Border Crossing (Belarus)
-Voivodeship Road DW 681 - Roszki-Wodźki - Łapy - Brańsk – Ciechanowiec
-Public transport
-Bus service
-Regular bus service is provided by Państwowa Komunikacja Samochodowa (State Car Communication, PKS) via PKS Bielsk Podlaskie, PKS Białystok and PKS Siemiatycze
-Rail service
-The closest passenger train service is provided by Polskie Koleje Państwowe (Polish State Railways, PKP) SA from the following stations:
-Szepietowo - express and local service to Warsaw and Białystok - 28 kilometres (17.4 mi) northwest
-Bielsk Podlaski - express and local service to Siedlce and Białystok - 25 kilometres (15.5 mi) east
Ⅲ.Economy
-Income
-Income data from 2005:
-Average per capita income: 1961.03 zł
-Compared to the average per capita income:
-In the Podlaskie Voivodeship: 120.40%
-In Poland: 112.20%
-The land-use is as follows:
-Agricultural use: 66%
-Forest land: 27%
-City: 2.34%
-Major business
-Financial: Banking - Bank Spóldzielczy w Brańsku, ul. Kosciuszki 2A, 17-120 Brańsk, Poland
-Manufacturing: Plastics - Wald-Gold, ul. M. Konopnickiej 20, 17-120 Brańsk, Poland
-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bra%C5%84sk#Economy
-http://www.bransk.podlaskie.pl/
Ⅳ.Industrial Characteristics
-The industrial characteristic of Brańsk is agriculture.
-Key projects
-1. "The government program to help disabled students in the form of co-financing the purchase of textbooks, educational materials and training materials in the years 2020 - 2022"
-"The government program to help disabled students in the form of co-financing the purchase of textbooks, educational materials and training materials in the years 2020-2022"http://www.bransk.podlaskie.pl/index.php/miasto-bransk/historia/8-aktualnosci/333-rzadowy-program-pomocy-uczniom-niepelnosprawnym-w-formie-dofinansowania-zakupu-podrecznikow-materialow-edukacyjnych-i-materialow-cwiczeniowych-w-latach-2020-2022
-2. Program "Toddler +" 2021
-Program"Toddler+"2021http://www.bransk.podlaskie.pl/index.php/8-aktualnosci/325-program-maluch-2021
Ⅴ.Attrations and Cityscape

-Places of worship
-Church of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary - Roman Catholic
-Parish serving Brańsk, Bronka, Brzeźnica, Glinnik, Jarmarkowszczyzna, Kalnica, Kiersnówek, Majerowizna, Oleksin, Otapy, Patoki, Popławy, Świrydy, Załuskie Koronne, Załuskie Kościelne
-Part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Drohiczyn
-St. Simeon Stylites - Polish Orthodox
-Mission church of Church of the Apostles St. Peter and Paul in Malesze
-Part of the Polish Orthodox Diocese of Warsaw-Bielsk
-Nearby attractions
-Sanktuarium Matki Bożej Pojedniania w Hodyszewie (Our Lady of Hodyszewo Sanctuary) in Hodyzewo - 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) northwest
Ossoliński Palace in Rudka - 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) west
Ⅵ.History and Culture
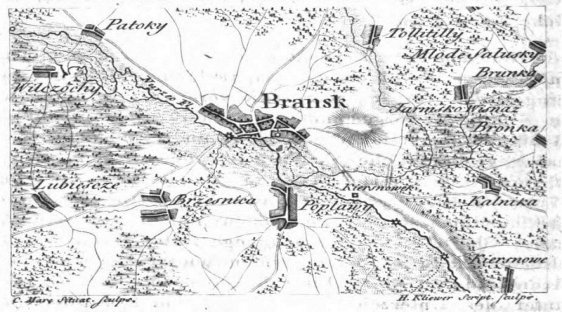
-BRAŃSK is a town in the Bielsko poviat of Podlaskie Voivodeship, picturesquely situated on the Nurzec River, on the route from Warsaw to Białowieża.
-The first time a man traveled to these areas was in the late Palaeolithic (about 10,000 years ago). Many archaeological sites have been discovered near the city confirming settlement throughout the ancient period. Particularly valuable are the Neolithic graves of the globe amphora culture (5,000 years), the oldest skeleton burial in this part of Poland and the treasure of bronze ornaments of the Lusatian culture (2,500 years).
-On the eastern outskirts of the city there is a historic wilderness called "Kumat" - considered to be the site of the battle of Polish troops led by prince Bolesław the Chaste, with the Jotvingians under the command of Komat in 1264.
-At the beginning of the city there was a stronghold built in the fork of the Nurzec and Bronka rivers in the 10th / 11th century, known today as "Zamczysko". Craft settlements developed near the stronghold, destroyed by the invasions of Ruthenians, Jotvingians, Mazovians and Lithuanians, and in the 14th century mainly by the Teutonic Knights. The first preserved documents mentioning Brańsk as the center of an unknown estate, managed by the governor of the Grand Duke of Lithuania, as a parish center come from the second quarter of the 15th century. At that time, Brańsk actively participated in the timber trade with Gdańsk. At that time, Mazovian settlers established many noble villages in the area (Popławy, Brzeźnica, Puchały, Płonowo, etc.), and Lithuanian-Ruthenian boyars settled in Kiersnów, Poletyła, Kadłubówka and others. Kmiece villages were subordinate to the Brańsk castle (Patoki, Oleksin, Holonki, Klichy et al.
-A good location near the road from Kraków to Lithuania and the border with Mazovia increased the importance of Brańsk. From 1422, land courts were held here. In the years 1440-1444, Brańsk was temporarily part of Mazovia and was the capital of the land. He could obtain the privilege of the reeve's office as early as around 1430 (the reeve and townspeople mentioned from the second half of the 15th century). On January 18, 1493 in Vilnius, from the hands of the Lithuanian Grand Duke Aleksander Jagiellończyk, Brańsk was the first town in Podlasie to receive full Magdeburg municipal law (Bielsk 1495, Drohiczyn 1498, Mielnik 1501 and Suraż 1445 with limitations, 1501). Since then, he has used the coat of arms "Pogoń". The townsmen of Brańsk studied at the Krakow Academy (from 1451).
-The 16th century was exceptionally successful in the history of Brańsk, the royal city. The activities of King Sigismund I and his wife, Queen Bona, were particularly marked here. For example, in 1532, the king began over 270 summer traditions of the Brańsk nobility assemblies. Bona helped the townspeople to free themselves from the exploitation of the Vilnius voivode, Olbracht Gasztold, she successfully opposed the idea of moving the land courts from Brańsk to Tykocin, and in 1550 she founded the hospital of St. Spirit and a poorhouse.
-In 1562, Brańsk was inhabited by about 1,800 inhabitants, there were 10 streets, two marketplaces, two Catholic churches with cemeteries, a parish school, an Orthodox church (from the end of the 16th century to 1839 Uniate church) with a cemetery, town hall, manor house royal, poorhouse, water mill with three wheels, brewery, malt houses, many craftsmen of various specialties.
-In 1569, during the Union of Lublin, the burghers of Brańsk were the first from Podlasie, on their own initiative, to ask the king to include the town in the Crown, which was welcomed by Sigismund August, giving the townspeople a special privilege. At that time, the farm economy developed in the district starosty of Brańsk. Significant surpluses in grain production were exported to Gdańsk. The starosts of Brańsk in the 16th and 18th centuries were, among others Leśniowolscy, Bogusław Radziwiłł, Branicki and Starzeniascy. The flourishing in the second half of the XVI and first half Crafts were going through the 17th century. There was a guild of shoemakers and tanners in the town, a large group of potters, thurses, bakers and salt traders.
-The accidents that took place in the autumn of 1628 in Brańsk echoed loudly in the then Commonwealth. The source of this was the sentencing to death by the municipal court and the execution of 26 noblemen - outlaws, who committed numerous murders and rapes in Podlasie. The execution was carried out in one day by a city executioner, which was an absolute Polish record. The skill of the executioner Michałek was the reason for the proverb: "And perhaps the executioner in Brańsk has bound you".
-The years of the wars in the second half of the The 17th and early 18th centuries. The city was largely destroyed. However, in the inspection of 1662 it was noted: "The city of Brańsk, the Bielsko-metropolis, where land and town rallies are judged, and all conventions and assemblies in the above-mentioned lands are held". It follows that despite the economic decline, Brańsk retained the rank of the administrative center of the Bielsko land, the largest of the three lands of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. The high administrative rank of the city meant that it hosted many Polish kings, magnates, politicians, people of culture, incl. Zygmunt Stary, Stefan Batory, Łukasz Górnicki, Bogusław Radziwiłł (starost of Brańsk), Stanisław Poniatowski - elected in 1761 at the sejmik in Brańsk as a deputy to the general parliament.
-Miasto was famous for the Monday markets and four annual fairs. In the 18th and 19th centuries, a post office operated in Brańsk on the route from Warsaw to Mitawa.
-In the years 1780-1817, Ignacy Kapica-Milewski, a well-known archivist and author of "Herbarz" of the Podlasie and Masovian nobility, worked in the Bran's land archive.
-After the third partition, Brańsk was under Prussian rule. The city had 1,145 inhabitants at that time. After the Treaty of Tylża in 1807, Brańsk became part of the Russian partition. The policy of the Russian partitioner deprived the old Polish administrative center of all the offices that gave it a supra-local rank. Brańsk was relegated to the role of a full-time city. In the second quarter of the 19th century, Brańsk was the seat of the Roman Catholic archdeacons of Białystok.
-In January 1826 in Brańsk there was the only major occurrence of the Decembrists in Poland. Officers and soldiers of the Sappers' battalion of the Independent Lithuanian Corps stationed here refused to swear allegiance to Tsar Nicholas I. The revolt was suppressed, and the leaders were sent to Siberia after the leniency of death sentences. The inhabitants of Brańsk actively participated in the national uprising in 1830 and 1863.
-The second half of the 19th century was a time of intensive demographic development of the city, mainly due to the increasing number of Jews settling in Brańsk, who in 1852 established their own community - the kehilla. In 1807, Jews constituted 7% of the total population, and in 1897 already 58% of the city's 4,087 inhabitants (35.3% Catholics, 6.3% Orthodox Christians, about 0.4% others).
-At the beginning of the 20th century, there was a Catholic church in Brańsk, an Orthodox church, as many as 6 Jewish houses of prayer (synagogues) and a yeshiva. Rabbi Szymon Szkop, one of the greatest experts in Judaism at that time, lived and worked here in the years 1906-1920.
-The First World War caused severe damage in Brańsk. Russian troops and many people evacuating deep into Russia passed through the city. Until mid-February 1919, the city was under German occupation. During the Polish-Soviet war, on July 30/31, 1920, a battle took place in Brańsk. On August 18, 1920, the city was liberated by the 1st Infantry Regiment of the legions.
-According to statistical data from 1921, Brańsk had 3,725 inhabitants (58% Jews, 40% Poles, 2% others) and was the third most populous city in the southern part of the Białystok Province. The city regained the status of a commercial center thanks to the revival of the Monday fairs. It was famous mainly for the horse trade. The Polish Red Cross Department running the municipal hospital of Królowej Belgijskiej, Volunteer Fire Department leading the brass band, Kasa Stefczyka, the Brańsk double warp carpets from the local factory were very popular. There were many other social organizations and craft workshops here. Easy contact with Warsaw and Białystok was possible thanks to Podlaskie Bus Lines running from Brańsk. In 1938, 4,594 people lived in the city.
-On September 7 , 1939, the city center was destroyed during a German air raid. On September 25, 1939, Brańsk was occupied by the Soviets, who incorporated the city into the Republic of Belarus. Until June 1941, several hundred people were repressed, including about 120 deported to Siberia. In June 1941, Brańsk was occupied by the Germans, who in November of the following year deported about 2,000 Jews crammed into the ghetto to Treblinka and killed there. The Germans established a forced labor camp for young Poles in the ghetto. The occupiers, retreating at the end of July 1944, burned down the church, bridge and the municipal power plant. In August, as a result of the Soviet provocation in Brańsk, the AK authorities of the Bielsk Podlaski district, concentrated here, were imprisoned.
-In the course of World War II the city was destroyed in 35 percent. In 1946, Brańsk had only 2,542 inhabitants. The local population has always been characterized by special patriotism and attachment to what is Polish and Catholic. Until the early 1950s, it was a strong center of the resistance movement against the new "people's" power (mainly AK-WiN - for example, "Łupaszka" with Lech Beynar, later known as Paweł Jasienica, a unit of "Huzar" and other groups, such as the NSZ), as a result of which deliberately hampered the city's development. The hospital, high school and independent dairy plant were closed.
-Pof 1970. There has been a slow development Brańska, soon halted a combination of administrative cities and villages into one body. In 1977, the city won the main prize in the national competition "Master of Economy", mainly due to the general order and commitment of the inhabitants. In 1992, thanks to the efforts of the inhabitants, the town and the commune were seceded. Since then, there has been a gradual catching up. A general secondary school was established, a sewage treatment plant with a network of sanitary collectors was built, a municipal stadium and a sports hall were built, other streets were drained, and the surfaces of the streets were improved. The construction of the reservoir is planned. The parish priest and parishioners thoroughly renovated the interior of the local parish church.
-Brańsk currently has 4,000 inhabitants. The city has vast areas (3243 ha, including 875 ha of forests), and the clean river Nurzec. People here are hospitable, described by others as ambitious and consistent. In the vicinity, the city itself is said to be "In Brańsk, you live your way". Visitors and passersby always pay attention to law and order and the unique atmosphere of the city.
Ⅶ.Other Information
-Brańsk [braɲsk] (Belarusian: Бранск, Ukrainian: Бранськ) is an Urban Gmina (Polish: gmina miejska) (Town) in Bielsk County, Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is located north-eastern Poland.
-The name of the town comes from the river Bronka, a nearby tributary of the Nurzec River.
Ⅷ.Contact Information
Mayor Eugeniusz Tomasz Koczewski
-Tel.: 085 73 75 940
-Fax: 085 73 75 363
-Email: sekretariat@bransk.um.gov.pl
