Lewin Brzeski-Opole 作者: 来源: 发布时间:2021-07-16
Ⅰ. Population and Area
Population (2019-06-30)
• Total 5,736
• Density 550/km2 (1,400/sq mi)
Area
• Total 10.35 km2 (4.00 sq mi)
Website http://lewin-brzeski.pl

Ⅱ.Natural Geography (environment and resources)
-Location of the Lewin Brzeski commune
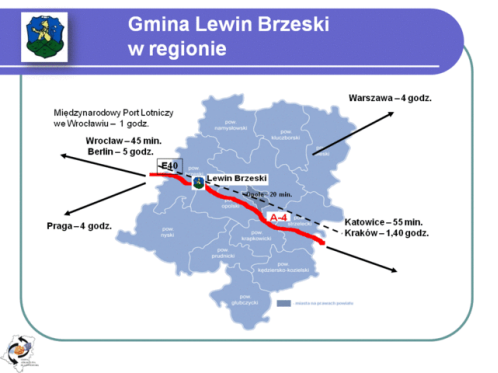
-The commune of Lewin Brzeski is situated at the estuary of the Nysa Kłodzka river to the Odra river, in the western part of the Opolskie Voivodeship, near the main communication routes of southern Poland. The A4 motorway runs along the southern edge, connecting the commune of Lewin Brzeski with Lower and Upper Silesia and Małopolska. The Odra River forms the border of the commune from the north.
-The commune covers an area of 15,970 ha, of which Lewin Brzeski - situated in its central part - occupies 1,035 ha.
-the market square in Lewin Brzeski1 The entire commune has almost 13.5 thousand inhabitants, of which the city is inhabited by less than 6 thousand people.
-The rural areas are divided into 20 villages: Łosiów, Strzelniki, Różyna, Jasiona, Leśniczówka, Buszyce, Skorogoszcz, Chróścina, Wronów, Mikolin, Golczowice, Borkowice, Błażejowice, Mała Nowa Wieś, Kantorowice, Sarny Małe, Stroszowice, Oldrzyszowice, Przecza and Ptecza .
-Population of the Lewin Brzeski commune
-Bridge over the Nysa Kłodzka river
-Communication
-An important communication route is the national road No. 94 connecting Wrocław with Opole, and then with Upper Silesia. The road runs through Strzelniki, Łosiów, Buszyce, Skorogoszcz and Borkowice.
-Lewin Brzeski has a good road connection with Nysa in the south of the Opolskie Voivodeship and with Kluczbork in the north.
-the bridge on the Odra River in Mikolin The second connection is provided by the only bridge crossing on the Brzeg-Opole section over the Oder in Mikolin. The commune of Lewin Brzeski has convenient road connections with the neighboring communes: Brzeg, Popielów, Dąbrowa, Niemodlin and Olszanka.
-Bridge over the Nysa Kłodzka river
-The A4 motorway from Berlin via Wrocław to Upper Silesia also runs through the commune. In the near future it will be one of the main road connections of Western Europe with the countries of Eastern Europe.
-The commune is crossed by the Wrocław-Katowice railway line, which also connects the south-western part of Poland with Upper Silesia. It runs through Łosiów, Lewin Brzeski and Przecza.
-Transport
-Lewin Brzeski is located on the Voivodeship Road DW458-PL.svg (northbound to Skorogoszcz and the National Road DK94-PL.svg; southbound towards Przylesie, where the road joins the Voivodeship Road DW401-PL.svg, northbound towards Brzeg and southbound towards the A4-PL.svg A4 Motorway then on). The interchange to the A4 autostrada (Poland) Motorway (Węzeł Przylesie) is located 20 km west of Lewin Brzeski.
-Lewin Brzeski lies on the main railway artery between Wrocław and Katowice/Lubliniec, with the town being served by Lewin Brzeski railway station.
Ⅲ.Economy
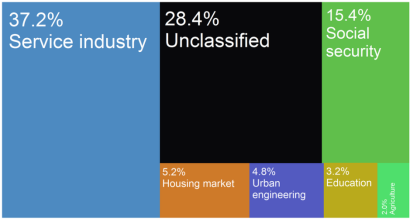
Lewin Brzeski city budget income sources as of 2015.
-Reliefs and investment facilities
-For entrepreneurs starting a business and creating new jobs, the following is exempt from real estate tax:
-usable areas of buildings or their parts;
-land surfaces;
-Structures related to economic activity.
-Exemption period:
-- For large enterprises - up to 5 years
-- For small and medium-sized enterprises - up to 3 years
-* The amount of the relief depends on the number of new jobs, eg 40 m2 of usable floor space in buildings, 200 m2 of land purchased for investment, PLN 20,000 of the value of the structure is released for 1 new job.
-WSSE
-Economic zone
-The Lewin Brzeski commune is in the process of creating a subzone of the Wałbrzych Special Economic Zone "INVEST PARK" in its area.
-Benefits of investing in "INVEST PARK":
- income tax exemption for income from business activities conducted in the zone;
-possibility of receiving public aid:
-Up to 50% of the investment costs or the costs of two years of employment of newly hired employees. Public aid: real estate tax exemption, financial resources from the Labor Fund, aid resources from European Union funds;
-Up to 50% in the case of obtaining public aid from various sources;
-Up to 50% for large enterprises, up to 60% for medium-sized enterprises and up to 70% for small enterprises.
-Planned creation of the zone - 1st half of 2008
-Why it will be worth investing in the Lewin subzone of the Wałbrzych Economic Zone "INVEST - PARK"
-system of tax reliefs and incentives,
-low labor costs,
-favorable geographic location,
-very well-developed communication network,
-extensive system of financial and banking services,
-qualified staff,
-availability of raw materials,
-a developed school system in the region,
-favor and assistance of local and government administration,
-Numerous tourist attractions.
-Plots proposed for the Lewin subzone "INVEST PARK"
-Lewin Brzeski - Urząd Miejski Lewin Brzeski http://lewin-brzeski.pl/6951/lewin-brzeski.html

The Lewin Brzeski Subzone of the Wałbrzych Special Economic Zone was established by the Regulation of the Council of Ministers of 28 July 2015
-The Lewińska subzone consists of 4 property complexes intended for the production, warehousing and storage area with a total area of 31.0391 ha.
-On 28 th of July 2015 the Council of Ministers approved the Lewin Brzeski subzone to include in Walbrzych Special Economic Zone.
-Lewin Brzeski subzone includes 4 complexes of properties for the production area storage, total zone’s land estimate 31.0391 hectares.
-Lewin Brzeski Subzone of the Wałbrzych Special Economic Zone - Lewin Brzeski City Hall http://lewin-brzeski.pl/3864/4579/podstrefa-lewin-brzeski-walbrzyskiej-specjalnej-strefy-ekonomicznej.html
Ⅳ.Industrial Characteristics
-Lewin Brzeski's economy is in large dependent on the local agricultural sector. The largest industry in the locality is the sugar mill "Wróblin". Surrounding the town there are five former gravel pits, now infilled by water, are a popular attraction for locals and people in the region alike. The town and its vicinity is home to numerous tourist attractions.
-Lewin Brzeski - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lewin_Brzeski#Economy
-Key projects
-1. Universal Agricultural Census 2020
-The mayor of Lewin Brzeski announces an open and competitive selection of candidates for field enumerators who perform activities as part of the census work related to the conduct of the agricultural census provided for in the Act of July 31, 2019 on the 2020 General Agricultural Census, who will perform census tasks in the area of Lewin Brzeski commune.
-2020 Agricultural Census - Lewin Brzeski Town Hall http://bip.lewin-brzeski.pl/9908/4804/powszechny-spis-rolny-2020.html
-2. Support for EU programs - FOR FISH 2014-2020
-A contract was signed for the construction of an administrative and technical building for the Community Fisheries Guard.
-Wsparcie programów UE - PO RYBY 2014-2020 - Urząd Miejski Lewin Brzeski http://lewin-brzeski.pl/8592/4762/wsparcie-programow-ue-po-ryby-2014-2020.html
Ⅴ.Attrations and Cityscape

Baroque Leopold's Palace, today a school

Memorial plaque to Polish officers Alojzy Józekowski and Kazimierz Niepla and other heroes of Polish independence struggles of 1939–1956
-Tourist attractions of the commune of Lewin Brzeski
-The landscape values of the commune include, apart from the Odra River Valley and the Nysa Kłodzka River Valley, smaller streams, sparse forests and ponds, from very large ponds to ponds, mid-field trees, as well as numerous cultural sites. Most of the villages are picturesquely situated with protruding silhouettes of church towers in the Gothic, Baroque and Neo-style styles.
-The silhouettes of manors and palaces with park complexes are visible from afar. The manor houses and the adjacent farms have retained the spatial layout of the street with an oval layout. One-storey residential, farm and farm buildings, situated at the gables with ceramic gable roofs, emphasize the characteristic value of the Opole village. The landscape values of the commune are shaped by the course and oxbow lakes of the Odra and Nysa Kłodzka rivers, forests constituting the buffer zone of the village and the Niemodlińskie Ponds.
-In the forest complexes in the eastern part of the commune, there is a protected landscape area called "Bory Niemodlińskie", which was created to protect the largest patch of natural vegetation and rich fauna of the left bank of the Oder in the Opolskie Voivodeship. Another area of interest for tourists is the "Stobrawski Landscape Park", which is a bird sanctuary of European importance. In the commune, the Park covers the Odra and Nysa Kłodzka valleys with forest complexes and oxbow lakes in the vicinity of Wronowo and Zawadno.
-Diversified and clean natural environment as well as excellent location makes the commune an attractive area for active forms of recreation. The Lewin Brzeski commune is characterized by a great wealth of stagnant surface waters. In this respect, it belongs to the richest municipalities of the Opole region. The attractiveness of these places is evidenced by the large number of visitors to water reservoirs, people living not only in the Opole region, but also in Lower and Upper Silesia.
-Between the fire tanks in Kantorowice, the commune of Lewin Brzeski has separated recreational plots intended for summer houses.
-These areas are developing very dynamically - in the last few years, a belt of small, brick and cozy summer houses has formed between the reservoirs. Their owners are people permanently residing in the Opolskie, Dolnośląskie and Śląskie voivodeships. The plots are approx. 3 ares, and their cost is approx. PLN 15 / m 2 .
-In the vicinity of the holiday plots, an area has been developed for service and catering activities, which is not yet fully developed by entrepreneurs.
-The two largest of them, located close to each other, near the town of Ptakowice, with a total area of 80 hectares, have an interestingly shaped coastline, conducive to rest for private individuals and for camping for organized groups. Between the reservoirs there is an area with separate recreational plots for individual buyers and about two hectares of land intended for a large recreational and leisure complex and a camping site.
-Within the city limits of Lewin Brzeski there is a water reservoir with an area of approximately 25 hectares, with a prepared place for bathing, sanitary facilities, parking and free areas for further development.
-In the south-eastern part of the commune there are ponds belonging to the complex of Ponds Niemodlińskie, one of the largest in the region.
-In the area of the commune, we find numerous traces of settlement and settlements of various cultures, cemeteries, and settlements from the 6th to the 15th century. Numerous archaeological sites and monuments testify to the rich and varied form of human life. The amber route from east to west and the trade route from Wrocław to Hungary ran through the commune. The first historical mention of Lewin comes from 1257, and it should be owed to the Joanite Monastery in Łosiów, where a commercial transaction concerning Lewin was concluded.
-The Lewin Brzeski Commune is crossed by a tourist route called "The Trail of Gothic Polychromes" in churches in Łosiów, Strzelniki, Różyn and Buszyce (unfortunately, during the last renovation, the polychromes were painted over).
-Lewin Brzeski also runs through the commune marked out81 km long bicycle trail . The route leads through the most interesting natural areas and covers the most important monuments of the commune. The course of the trail, in order to increase the attractiveness as well as for the greater safety of cyclists, was marked out mainly by dirt roads, through rarely frequented areas.
-Gravel water reservoirs that cross the commune of rivers, oxbow lakes and ponds are very attractive for fishermen and supporters of other forms of recreation by the water.
-Kantorowice nature and landscape complex
-Lewin Brzeski Palace Kantorowice
-Kantorowice hunting castle
-Wronów Palace
-Łosiów Palace
-Lewin Brzeski nature and landscape complex
- Kantorowice nature and landscape complex
-Kantorowice nature and landscape complex
-Recreation area at ZPK Kantorowice
-Manor house in Mikolin
-Kantorowice nature and landscape complex
-The bicycle trail board at the Zawadno State Agricultural Farm
-Towns of the Lewin Brzeski commune:
-Błażejowice
-Borkowice
-Buszyce
-Chróścina
-Golczowice
-Jasion
-Kantorowice
-Łosiów
-Forester's lodge
-Mikolin
-Nowa Wieś Mała
-Oldrzyszowice
-Ptakowice
-The hamlet of Raski
-Rose
-Little Roe Deer
-Skorogoszcz
-Stroszowice
-Shooters
-Wronów
Ⅵ.History and Culture
-Located along the medieval trade routes from Silesia to Hungary, by the Amber Road and the Eastern Neisse river, the town of Lewin first developed in the Middle Ages as a market town, located within the Piast-ruled Kingdom of Poland and as a result of the fragmentation of Poland it became part of the duchies of Opole, Brzeg and Legnica. It is first mentioned in a contract from 1257, when a monastery run by the Knights Hospitaller in Łosiów purchased a mill near the town. Its name is of Old Polish origin and refers to hunting. As early as the mid-13th century the city had received Magdeburg town rights, which granted the town a certain amount of autonomy. The town was built around a rectangular marketplace, and surrounded by a rampart with a palisade with a ditch below it that could, if necessary, through the opening of a lock could be filled with water from the Eastern Neisse. In addition, there were four city gates. In 1333 the town was granted new rights and privileges, such as the brewing of beer and the holding of Wednesday markets, by Duke Bolesław III the Generous. Lewin switched between the duchies of Legnica and Brzeg and remained under the rule of the Piast dynasty until 1675, although it fell under the suzerainty of the Bohemian (Czech) Crown in 1329, Hungary in 1469, and again Bohemia in 1490, then ruled by the Jagiellonian dynasty until 1526 and the House of Habsburg afterwards.
-Historical architecture on the Market Square
-The 16th century brought an economic boom to the city. Since 1592 yearly fairs were organized with the permission of the duke of Brzeg. After the Reformation the town became mainly Protestant, and the Catholic parish was disbanded. During the Thirty Years' War the town was looted, burned, and struck by the Plague. After the dissolution of the Duchy of Legnica in 1675, it was incorporated into the Habsburg Monarchy.
-In 1742, under the Germanized name Löwen, it became part of Prussia, by then a town of almost 700 people. Several town fires burned the city, the most devastating in 1829, which destroyed the wooden buildings completely and ushered in a fundamental reconstruction of the city. The city was rebuilt with stone buildings, such as the neoclassical Town Hall built in 1837 at the Market Square. In 1846 Löwen was attached to the Upper Silesian Railway, which brought a revival of industry to the city. In 1866 a metal factory was founded, which produced at first agricultural equipment, then screws, and, much later, finally tape recorders. Other industries included a brick factory, a roof and floor tile factory and a mill. In 1866 the Catholic parish was reestablished, though the St. Mary's Church was not built until the early 20th century. In 1901 the village of Fröbeln, which had a sugar factory since 1882 and population of 554 inhabitants in 1885. Administratively, Löwen was located in Landkreis Brieg, and the seat of its own local court. The old, dilapidated bridge over the Neisse was replaced in 1913 by a new steel bridge.
-Pond in Lewin Brzeski
-During World War II the Germans brought hundreds of forced labourers to the town, mostly Poles, but also Russians, Ukrainians, the French, Jews ans Serbs, both civilians and prisoners of war. In the final stages of World War II, in January 1945, the Germans evacuated most of the population, leaving only the elderly in the town, and recruited many inhabitants into the Volkssturm. On 4 February 1945 the town was overtaken by the Red Army, which plundered it afterwards.
-After the Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland during and after World War II the town was transferred to Polish control and its historic name Lewin was restored, with the adjective Brzeski added after the nearby city of Brzeg. It was repopulated by Poles, some of thems expellées from former eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, in particular from pre-war southeastern Polish regions Stanisławów and Lwów. It was first administered as part of Wroclaw Voivodeship and in 1950 the city was moved to the Opole Voivodeship, where it has remained despite the administrative reforms of 1999. In the years 1950–1953 a secret anti-communist organization Podziemny Orzeł Wolności ("Underground Eagle of Freedom") operated in the town Its co-founder, Mieczysław Józefczyk, was awarded the Knight's Cross of the Order of Polonia Restituta, one of the highest Polish decorations, in 2017.
-A monument of Pope John Paul II was unveiled in Lewin Brzeski in 2014.
Ⅶ.Other Information
-Lewin Brzeski is a town in Brzeg County, Opole Voivodeship, Poland, with 5,736 inhabitants (2019).
-The coat of arms of Lewin was adopted on 18 June 1998 and was based on a seal from the year 1333. It shows a golden lion bordered by three hills on a blue background. The lion recalls the old German name Löwen, which means "lions".
Ⅷ.Contact Information
Mayor Artur Kotara
Town Hall of Lewin Brzeski49-340 Lewin Brzeskiul. Market 1
Phone: 77 424 66 00
E-mail: lb@lewin-brzeski.pl
